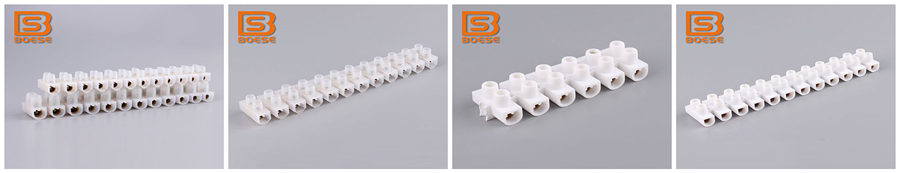
What is a terminal block?
In electrical connections, a terminal block acts as a crucial bridge that secures and connects wires, ensuring stable current transmission in various systems. Whether in industrial control cabinets, household appliances, or new energy equipment, this small but mighty component plays an irreplaceable role. Let’s explore the basics of terminal blocks, including their types, common uses, material features.
What is a Terminal Block?
A terminal block is an electrical component designed to connect multiple wires safely and efficiently. It provides a standardized interface for wire termination, preventing short circuits and simplifying maintenance. Unlike direct wire-to-wire connections, a terminal block allows easy disconnection and reconnection, making it essential for systems requiring frequent adjustments or repairs.
Common Types of Terminal Blocks
Terminal blocks vary by structure and application, with three main types widely used:
•Screw Terminal Blocks: The most traditional type, using screws to clamp wires. Ideal for heavy-duty industrial use due to strong connection stability.
•Plug-in Terminal Blocks: Feature a plug-and-socket design for quick installation/removal, perfect for equipment needing frequent maintenance (e.g., medical devices).
•Spring Terminal Blocks: Use spring force to secure wires, eliminating the need for tools. Popular in household appliances and light industrial settings for time-saving installation.
Key Uses of Terminal Blocks
Terminal blocks are indispensable across industries:
•Industrial Automation: Connect sensors, motors, and controllers in factory control cabinets.
•Household Appliances: Secure wiring in refrigerators, air conditioners, and washing machines for safe operation.
•New Energy Systems: Link solar inverters and battery storage units, ensuring reliable energy transmission.
•Building Electrical: Simplify wiring in lighting systems and power distribution boxes.
Material Features: Why Plastic Matters
The housing material of a terminal block directly affects its safety and durability, and plastic is the preferred choice for several reasons:
•Insulation Performance: High-quality plastic (like PA66 used by BOESE) resists electricity, preventing leakage and short circuits.
•Heat Resistance: Flame-retardant plastic materials (compliant with UL94 V0 standard) withstand high temperatures up to 120°C, suitable for harsh environments.
•Lightweight & Cost-Effective: Plastic reduces overall weight compared to metal housings, lowering transportation costs without compromising strength.
•Corrosion Resistance: Unlike metal, plastic resists rust and chemical damage, extending the terminal block’s lifespan.
Summary
A terminal block is more than just a wire connector—it’s a cornerstone of electrical safety and efficiency. With types tailored to industrial, household, and new energy needs, and plastic materials offering superior insulation and durability, it’s vital for reliable connections. BOESE terminal blocks, combining quality materials and innovative design, provide solutions for diverse wiring challenges.
Need a reliable terminal block for your project? Contact BOESE today for customized solutions! For more electrical component guides.